A CRM Model design for Customer Services in Bank Sector
Introduction
Customer relationship management is a broad concept for creating, retaining and expanding customer relationships in banking sector. There are probably five different answerers, when five different banking officers were asked about their views on Customer Relationship Management. CRM is not just a single application that will solve all customer related problems in an organization. Rather, CRM is almost a “state of mind” within an organization in which three key functional areas of the organization are integrated. These areas are sales, marketing and customer service.
The market became much more clear for customer because of new media. The results are an increasing pressure of competition and demanding customer. Therefore a binding and long-term customer relationship seems to be necessary in banking sector. In modern era, the ability to maximize customer reliability, consistency and durable relationships is critical in banking sector. As banks strive to create and manage customer relationships, several emerging trends affect to approach and tools. Banks employ to achieve sustainable growth. These trends reflect a fundamental change in the way that banks interact with the customers what they have and those they want to require.
The idea of CRM is that it helps businesses use technology and human resources gain insight into the behavior of customers and the value of those customers. If it works as hoped, a business can: provide better customer service, make call centers more efficient, cross sell products more effectively, help sales staff close deals faster, simplify marketing and sales processes, discover new customers, and increase customer revenues. It doesn’t happen by simply buying software and installing it. For CRM to be truly effective, an organization must first decide what kind of customer information it is looking for and it must decide what it intends to do with that information. For example, many financial institutions keep track of customers life stages in order to market appropriate banking products like mortgages or IRAs to them at the right time to fit their needs. Next, the organization must look into all of the different ways information about customers comes into a business, where and how this data is stored and how it is currently used. One company, for instance, may interact with customers in a myriad of different ways including mail campaigns, Web sites, brick-and-mortar stores, call centers, mobile sales force staff and marketing and advertising efforts. Solid CRM systems link up each of these points. This collected data flows between operational systems and analytical systems that can help sort through these records for patterns. Company analysts can then comb through the data to obtain a holistic view of each customer and pinpoint areas where better services are needed.
In current situation of competitive banking world, improvement day-by-day in customer service is the most important tool for their better growth. Banking companies are increasingly adopting customer-centric strategies as a means of maintaining and enhancing their competitive advantages. CRM is concept that requires a new customer centric business model which focuses on the seamless integration of every business that touches the customer. In this study a model of CRM in banking sector is designed, reflecting Customer Database, Analysis, Action plan and Implementation. Many banks have used CRM tools to acquire more customers and to improve relationships with them. Banking companies are increasingly adopting customer-centric strategies as a means of maintaining and enhancing their competitive advantages. The idea of CRM is that it helps banking sectors use technology and human resources gain insight into the behavior of customers and the value of those customers. The need for the study arises because banking sector helps in economic development of the country and to fulfill this, customer satisfied first by providing better services with the help of computer and other innovated technologies. Hence there is need for customer survey, identifying their requirements and satisfaction.
Literature Review
D.Gopalakrishna (2001) expressed his views that Customer relationship is not an outside element which started exerting its influence on the business. It is an integral part of management and of late, it has occupied an important and indispensable central place in today’s business. MH Peeru Mohamed & A Sagadevan (2005) Managing relationship with customer and making them delighted has become a necessity in the wake of globalisation, where customer delight is the only key to success and to the very existence of the company.
Nils Merkel (2005) stated the expectations from companies in the banking sector and requirement of a successful implementation of CRM. For a successful implementation, there must be a common sense that the implementation will affect all parts of the company and that there might be server changes to get positive results. Due to that the project must be supported by the management from the very beginning.
Umesh C.Patnaik & Basudev Chhatoi (2006) Customer Services will be better understood if we define it from the customer’s angle. Customer service is the perception of a customer regarding the services he gets from his bank. It is found that retaining customer is often cheaper than finding a new customer. Customer is viewed as a long-term relationship. Graham Roberts-Phelps (2008) explains that there are three elements to consider when aligning your business towards a customer relationship format. These are retention, customer potential and de-selection of customer. He also mentioned four steps if CRM i.e. Segmentation, Analysing, Developing strategy and Behaviour maintenance.
R.K.Uppal (2008) CRM in the Indian banking system is fundamental to building a customer-centric organization. CRM systems link customer data into a single and logical customer repository. CRM in banking is a key element that allows a bank to develop its customer base and sales capacity. The goal of CRM is to manage all aspects of customer interactions in a manner that enables banks to maximize profitability from every customer.
Objectives of the Study
The study is primarily to understand the contribution of Customer Relationship Management in banking sector and its impact and reality.
- To assess the awareness of CRM in banking sector.
- To develop a Customer Service Model for bank.
- To analyses on decision making activity by banking sector.
- To motivate long-term reliability in the terms of relationship with customer.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of complaint request management of bank.
- To increasing lifetime value of individual customer through CRM.
Hypothesis
There is a large scope for the development of banking sector with the help of CRM and proper utilize for customer service model.
Research Methodology
In present paper, I briefly summarize some of key concepts and frameworks of customer relationship management in banking sector. This research is based on secondary data. The scope of the present study is restricted to analyses the CRM and develop a Customer Service Model for bank. The secondary data has been collected from internet and books.
Analysis
In order to evaluate the role of customer relationship management, let us first confirm that banking has to do with providing services time to time, which is largely what customer require that they are doing. CRM is a sound business strategy to identify the bank’s most profitable customers and prospects, and devotes time and attention to expanding account relationship with those customers through individualised marketing, reprising, discretionary decision making, and customised service through the various sales channels that the bank uses.
A Customer Service Model for Bank
Customers have invested their time and sought services from bank because they believe that you can satisfy their desires. Attrition is the key indicator in measuring the success of any retention and customer service strategy. Each bank will have to its own customer service model that relates the customer support and satisfy the customers need and solution a there problem, which also feels in some way special. Following is a model that one can believe works when it comes to customer service. Customers who contact bank will only ever need or want two things they need a solution to a problem and they want to feel in some way special. The following figure 5.2 shows Customer Service Model.
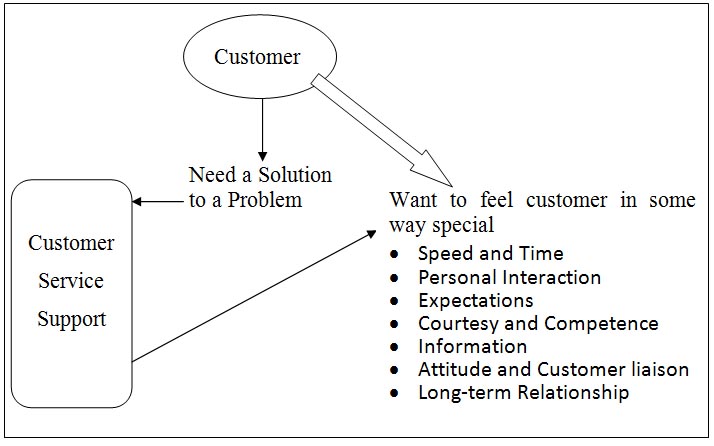
Bank should provide a physical or a psychological solution to customers real or imagined problem. Very often the only time the customer contact the bank is when they have a problem with something they required service. Therefore customers need should be put right and the better that they are put right most satisfied the customers is going to be and every single customer has to feel in some way special. There can be seven most important elements in making a customer feel special over and above solving their initial problem or basic concern. By some strange coincidence, when put together these seven elements will actually spell the word special.
- Speed and Time: Speed and time measures are very important factors to many customers. The speed with which your company or organisation can deliver, whatever it is it provides, can actually gain you competitive advantage and allow bank to offer higher satisfaction, and maybe even demand, or ask a price premium from your customers for that convenience of doing things faster or quicker. However it is not just about the core product, it is also about every single contact or initiation with a customer, from answering the telephone, to replying to letters, to the length of a phone call, to how long bank have been put on hold. The customer measures all these factors, largely unconsciously.
- Personal interaction with a customer: How well and how able an organisation does this varies from the small to the large. A small detail matter, remembering a customer name, a tone of voice and remembering details about that customers.
- Expectations: The ability to manage expectations well and then systematically and consistently exceed them is the hall mark of a successful business. There are only three kinds of physical and emotional states that one can leave customers in a delighted happy customers, a satisfied customer and a dissatisfied customer. Applying the process of managing and then exceeding expectation is one that can happen randomly and through the creative ingenuity of a few customers focused individuals, but is really should not be left to chance.
- Courtesy and competence: The two go hand in hand. Statistics show that customers seem to be happier being served by an enthusiastic amateur rather than an indifferent expert. Common courtesies and manners are very important, probably more important than one may consider at this point. Competence means that whoever serves the customer in bank or whoever supports people that serve customers in bank has to do things and do then well.
- Information and keeping the customer informed: The current era is a much more complicated place than in the past. Technology, social changes and education patterns have created a mass of information. One of the simplest ways to keep customers feeling special and make them feel important to bank is to keep them informed. Keep them informed of things they are waiting for and let them know how things are going. If there is an expectation that is going to be broken or damaged then let them know as soon as bank know.
- Attitude and customer liaison: Attitude is not always easy to understand, train or instill. So let us look at what sort of attitude that mean. It is generally defined as a positive enthusiastic and helpful attitude – somebody that seem more alive than dead, it means somebody who seems to enjoy what they do or enjoys dealing with customers, not just somebody who happens to do this as a job to earn a living. Even though this may be true, a good customer service experience is one where the customer service person pretends if nothing else, that they enjoy their job and they like doing what they do and they are pleased to see the customer. One of the most important aspects of attitude is when the customer is dissatisfied. The customer will then seem to view life through a telephoto lens and every detail or every aspect of the interaction will come under scrutiny. Therefore, the attitude must be to look at a glass of water as half full, instead of half empty.
- Long-term Relationship: This is final element of making a customer feel special. A customer will feel special if the organisation that they have dealt with once or just a few times will actually reward, recognize and encourage their loyalty. This will not work with every customer and some customers are rampantly and consistently disloyal. However, for the majority of customers, either business or personal, given the right elements and environment they would prefer to be consistent. Indeed many people think that the drive for consistency in sameness is one of the strongest human instincts of all, perhaps more so than survival. This explains why so many organisations that offer seemingly poor service and low levels of customers satisfaction seen to survive. It is because they exploit the customers consistency drive and often customers with rationalise to themselves.
When put together each one of these seven elements will accelerate customer satisfaction beyond even their wildest dream. They need to become a constant preoccupation to the customer focused business. Bank should be implement ideas based around seven elements and make them a constant focus of attention, it will become unerringly more customer focused and customers will become increasingly more loyal and profitable. A customer that feels special will spend more.
Conclusion
CRM in banking is concerned with attracting, maintaining and enhancing customer relationship. CRM goes beyond the transactional exchange. Customer can be provided with products and services effective relationship. CRM is depended upon banking employees with proper utilization of services and their behavior. We know that providing effective and efficient service is essential not only to attract new customers, but also to retain existing customers. Current banking sector has come up with a lot of initiatives that are oriented to providing a better customer service with the help of new technologies. Bank must explore and alter the process with the help of model by which customer information captured through database, analyzed, evaluation, action plan, implementation and wait for results. CRM is important in the banking sector. Banks are realising that CRM is the magic bullet that helps financial institutions to build stronger and more profitable relationships. The banks can adopt a Customer Service Model for better CRM practices, as it is believed that products should be devised for the customers or can design and follow a model process. Banks must build their brand image in assuring customers about the safety of their money and security of transaction on the Net. Hence rather than focusing on developing product strategies, banks can deliver to customers by having a concise and precise ways of doing things through effective CRM.
Reference
- T.Aher (2012), Customer Relationship Management A Case Study, .IJBMB, pp.40-45
- Constantin Zopounidis (2002), New Trends in Banking Management. Physica-Verlag, New York.
- Gopalakrishna (2001), Electronic Marketing in 21st Century. Himalaya Publishing House, New Delhi.
- D.Bhakkad (2011), Success factor of CRM in Banking Sector. Banking Finance, Kolkatta, pp.9-12
- D.Bhakkad (2011), CRM in Banking Sector : Impact and Reality. Research Link, Indore.
- Graham Roberts-Phelps (2008), Customer Relationship Management. Viva Books Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
- Peeru Mohamed & A.Sagadevan (2005) Customer Relationship Management. Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.
- Leonard L. Berry (1995), Relationship Marketing of Services- Growing interest Emerging Perspectives, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Sciences, pp. 236-245.
- P.Jaisawal & Anajli Kaushik (2002), E-CRM : Business & System Frontiers, Asian Books Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Manoj Patwardhan (2009), CRM in Indian banking Sector: exploring the critical success factors, International Journal of Business and Emerging Markets 2009 – Vol. 1, No.3 pp. 282 – 295, 2009
- Nils Merkel (2005) Customer Relationship Management in Banking Sector. Books on Demand GmlbH, Germany.
- K.Uppal (2008), Customer Relationship Manage ment in Indian Banking Industry. New Century Publications, New Delhi
- Umesh C.Patnaik & Basudev Chhatoi (2006), Bank Marketing. Sonali Publication, New Delhi.
Author
Dr.Dinesh D.Bhakkad
Asstt.Professor & Research Guide
P.G. & Research Department of Commerce
S.P.D.M.College Shirpur Dist.Dhule (MS)
Published : Banking finance Magazine, February, 2013 Issue.


